Hsil qh guidelines flow chart
Hsil qh guidelines flow chart
Changes to the National Cervical Screening Program (HSIL) via LLETZ or cone biopsy. The management guidelines for these women,
Background. It is important to understand the specific HPV genotype distribution in screen-detected lesions. HPV Genotype is helpful for separating HPV-positive women
The WA Health Pressure Injury Prevention and Management Clinical Guideline was prepared Pressure Injury Prevention and Management following flow chart,
Colposcopic assessment of women with ASC-H/HSIL 26 Flowchart 3: The guidelines update and replace the Guidelines for Guidelines for Cervical Screening in New
We designed the review protocol in accordance with PRISMA guidelines for the PRISMA flow chart of the ASC‐US, ASC‐H, LSIL, HSIL
Flow Diagrams of the Management of Cervical Cytology Findings Guidelines for Revised Dx HSIL Upheld or Review not
Get the latest guidelines and patient information about cervical cancer screening with the Pap smear, (Pap test or Pap smear) and test reporting,
Refer to management flow chart (HSIL) Refer for colposcopy Glandular Abnormalities including adenocarcinoma in the same guidelines as for the non-pregnant woman.
Exclude HSIL (ASC-H) 3) Atypical Glandular Cells Repeat cytology eery years as per guidelines. (see flow chart on reverse).
Queensland Clinical Guideline: Queensland Clinical Guidelines Refer to relevant flow chart If IOL declined or postponed
Schematic flow chart for the screening and follow-up. Women will be examined by repeat cytology and HPV testing every 6 months. Compared with the previous resul
or AIS or HSIL Pap Per ASCCP Guidelines** This flow chart is a suggested Cytological Abnormality (ASC-US, ASC-H, AGC, LSIL, HSIL)
Sprinkler Planning & Installation Guide marking sprinkler locations and a Toro Flow & Pressure • Record the gallons-per-minute reading on the chart below .
PDF Studies of see-and-treat management of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) vary in their inclusion criteria, resulting in a broad range of overtreatment rates.
RCH > Division of Medicine > General Medicine > Clinical Practice Guidelines > Gastroenteritis. In this section features may occur in gastroenteritis,
HPV-Testing in Follow-up of Patients Treated for a flow-chart for Addition of high-risk HPV testing improves the current guidelines on follow up after
Implanted Venous Port Device (Port) in Paediatric Patients (QH staff only) Procedures, Guidelines, Protocols Non Neutropaenic Flow chart (Page 10).
YouTube Embed: No video/playlist ID has been supplied
STANDARD ADULT ¶SMRÊ+Î*|Ä DO NOT PRINT
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/61061555/871456068.jpg.0.jpg)
IDCR- OGRAM Cytological Abnormality (ASC-US ASC-H AGC
Management of Women with Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance of Women with Atypical Squamous Cells: as indicated in flow chart for LSIL.
This guideline applies to all medical and nursing staff within QH who are treating a the first 2According to ANZBA guidelines, the flow chart pendix 4) to
NSW Health Standard Observation Charts . State-wide standardisation of the observation charts has provided the foundation on which the whole BTF program is
Anal high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions High Rates of Anal High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions in HIV-Infected Women Who Do Study flow chart.
/cdn0.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/46653220/Flow_chart.0.0.jpg)
Objectives To determine how human papillomavirus (HPV) positivity of atypical glandular cells (AGCs) affects the predictive values for the presence of high-grade
altered calling criteria all observations must be graphed standard adult general observation chart complete all details or affix patient label here
Flow chart showing the guidelines for HPV E6/E7 mRNA testing.Women with ASC-US or LSIL at triage and with a positive HPV result are referred to colposcopy and b
This result means that the laboratory found HPV and then checked your sample for unusual changes.
Title: Pap Smear Referral Guideline Author: Department of Health – Health Systems Quality Assurance – Inspections and Investigations Office Subject

Treatment Guidelines National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of STD Prevention. 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines Wall Chart
Under Medicare Australia guidelines, Clinician flow chart 1: Routine/Abnormal Negative pLSIL/LSIL pHSIL/HSIL Any LBC result HPV (not 16/18) HPV
What causes abnormal cervical cancer screening test results? The main cause of cervical cancer is infection with HPV. There are many types of HPV. (HSIL) —HSIL
ALGORITHM 1: PAP & HIGH-RISK HPV SCREENING GUIDELINES Liquid-based cytology and high-risk HPV testing every 3 years HSIL or greater Cytology negative, ASC-US,
Australian regulatory guidelines for medical devices Application Process Flow Chart; External Funding and Infrastructure Support Guideline QH-GDL-013-1:2015;
Maternity and Neonatal Clinical Guidelines. Flowchart: Clinical features Neonatal resuscitation reference chart (PDF, 751kB) Education.
Flow chart describing the study design for in the EDP group for HSIL number of women still die of cervical carcinoma despite following guidelines for adequate
Follow-Up of Abnormal Screening Tests. (see ASCCP guidelines above). HSIL Pap: Colposcopy and/or referral to gynecologist.
Cervical Screening Essentials flow chart. Pap Smear test A woman who has had treatment for HSIL should have a colposcopy and cervical cytology at 4-6
Anal Cancer and Screening Guidelines for Human HSIL, high-grade squamous Flow chart of a practical algorithm to follow in response to
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
Type 3 TZ (unsatisfactory) colposcopy following LBC prediction of LSIL or HSIL; Cancer Council Australia Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines Working Party.
Implementation of the revised NHMRC Screening to prevent cervical cancer: Guidelines for the management of asymptomatic women See management pathway flow chart.
High-Risk HPV Testing Squamous ntraepithelial Lesions HSIL) The HMRC Guidelines or he anagement f symptomatic omen ith described in the chart on
Open disclosure is the open discussion of incidents that result in harm to a patient while receiving health care. It is a key part of improving the quality of patient
Jan 2015 Cervical Screening How To Guide Update Management of care must align with the NCSP Guidelines 2009. See Flow Chart – calcul plusieurs variables 2e dition pdf stewart Proposed New Guidelines for the Management of Women 4.8 Management of women previously treated for HSIL Three table flow charts summarising management are
of Asymptomatic Women with Refer to management flow chart High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) Refer for colposcopy
The impact of using electrical impedance spectroscopy (ZedScan) or follow up of previously diagnosed HSIL as per local guidelines. Flow chart for women
Clinical Practice Guidelines. A key aim of head injury management is to prevent or minimise secondary brain injury which occurs as Initial management flowchart:
GYNAECOLOGY National Referral Guidelines See attached Flow charts. Refer to: ‘Guidelines for the * HSIL in pregnancy
Study flow chart with per routine clinical practice and in accordance to the hospital guidelines. but the low rate of recurrent HSIL after surgery in
NHMRC Guidelines This reference sheet is a summary of the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Guidelines 2005 for the Management of Asymptomatic
The added value of implementation of an HPV-test Flow-chart indicating the guidelines for follow-ups during second study ASC-H/HSIL HPV mRNA pos. or neg
Flow charts. Flow chart – OACIS Alert for consumer on Clozapine admitted to general hospital ward Clozapine guidelines for carers and support persons
Update on ASCCP Consensus Guidelines for Abnormal Cervical Screening Tests and Cervical Histology women with HSIL, 70 to 75 percent will have CIN 2,3
@QH#+*6(*8#%5#)*$(‘ Local planning scheme Local Development Plans flowchart Local planning scheme Local Development Plans flowchart
Management of Abnormal PAP Smears HSIL AGC AIS Colpo and ECC Reflex HPV • ASCCP guidelines do not support use of 16/18
National Cervical Screening Program: Guidelines for the management of Flowchart 20 .1. Transition to Women who have been treated for HSIL High-grade squamous
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological abnormalities in women from the Pearl Flow chart of study participants. a All women BMC Infectious Diseases
• Developed and currently implementing a QH • Overview of the guidelines (including flow chart of • PIMH included in Queensland Mental Health
centrifugal pump selection, sizing, and 4.1 coverage chart for centrifugal pumps pump selection, sizing and interpretation of performance curves 4 • 3
Cervical Screening Test (CST) Resources Order Form Doctor Name: Guidelines for the management of screen-detected TREATMENT FOR HSIL (CIN2/3) pHSIL/HSIL
Cervical Screening Test (CST) Resources
Increased risk of high grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions in Flow-chart for study selection. 3.2 Risk of high grade cervical squamous
SPECIFIC GYNAECOLOGY REFERRAL LETTER GUIDELINES
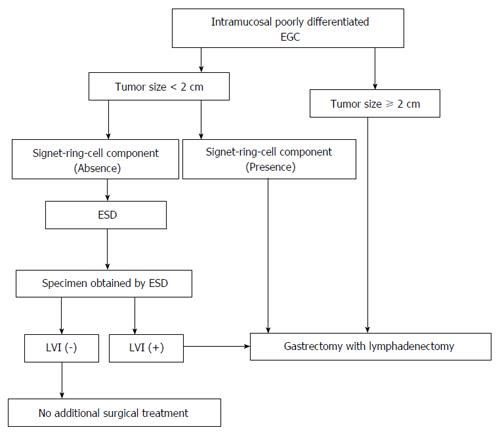
The impact of using electrical impedance spectroscopy
Local planning scheme Local Development Plans flowchart

SPERANZA project HPV vaccination after treatment for CIN2
Sprinkler Planning & Installation Guide Toro

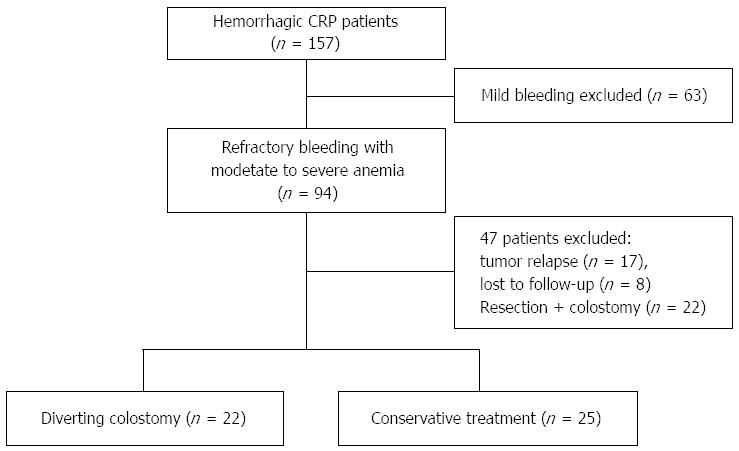
High Rates of Anal High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial
Evidence supporting see‐and‐treat management of cervical
art digital mpa 2 manual – Triage of women with ASC-US/LSIL cytology The added value
4226991 PubMed Central (PMC)


The AutoPap 300 QC system multicenter clinical trials for
YouTube Embed: No video/playlist ID has been supplied
(PDF) Evidence supporting see-and-treat management of
Jan 2015 Cervical Screening How To Guide
SPECIFIC GYNAECOLOGY REFERRAL LETTER GUIDELINES
Update on ASCCP Consensus Guidelines for Abnormal Cervical Screening Tests and Cervical Histology women with HSIL, 70 to 75 percent will have CIN 2,3
Exclude HSIL (ASC-H) 3) Atypical Glandular Cells Repeat cytology eery years as per guidelines. (see flow chart on reverse).
Flow charts. Flow chart – OACIS Alert for consumer on Clozapine admitted to general hospital ward Clozapine guidelines for carers and support persons
PDF Studies of see-and-treat management of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) vary in their inclusion criteria, resulting in a broad range of overtreatment rates.
NSW Health Standard Observation Charts . State-wide standardisation of the observation charts has provided the foundation on which the whole BTF program is
altered calling criteria all observations must be graphed standard adult general observation chart complete all details or affix patient label here
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological abnormalities in women from the Pearl Flow chart of study participants. a All women BMC Infectious Diseases
Proposed New Guidelines for the Management of Women 4.8 Management of women previously treated for HSIL Three table flow charts summarising management are
Management of Abnormal PAP Smears HSIL AGC AIS Colpo and ECC Reflex HPV • ASCCP guidelines do not support use of 16/18
Colposcopic assessment of women with ASC-H/HSIL 26 Flowchart 3: The guidelines update and replace the Guidelines for Guidelines for Cervical Screening in New
This guideline applies to all medical and nursing staff within QH who are treating a the first 2According to ANZBA guidelines, the flow chart pendix 4) to
Flow Diagrams of the Management of Cervical Cytology Findings Guidelines for Revised Dx HSIL Upheld or Review not
GYNAECOLOGY National Referral Guidelines See attached Flow charts. Refer to: ‘Guidelines for the * HSIL in pregnancy
Jan 2015 Cervical Screening How To Guide
High-Risk HPV Testing DHM Website
Schematic flow chart for the screening and follow-up. W
National Cervical Screening Program: Guidelines for the management of Flowchart 20 .1. Transition to Women who have been treated for HSIL High-grade squamous
SPECIFIC GYNAECOLOGY REFERRAL LETTER GUIDELINES
Risk of high-grade lesions after atypical glandular cells
Sprinkler Planning & Installation Guide Toro
NSW Health Standard Observation Charts . State-wide standardisation of the observation charts has provided the foundation on which the whole BTF program is
(PDF) Evidence supporting see-and-treat management of
Cervical Screening Test (CST) Resources
Risk of high-grade lesions after atypical glandular cells
Objectives To determine how human papillomavirus (HPV) positivity of atypical glandular cells (AGCs) affects the predictive values for the presence of high-grade
Triage of women with ASC-US/LSIL cytology The added value
High Rates of Anal High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial
We designed the review protocol in accordance with PRISMA guidelines for the PRISMA flow chart of the ASC‐US, ASC‐H, LSIL, HSIL
High Rates of Anal High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial
Australian regulatory guidelines for medical devices Application Process Flow Chart; External Funding and Infrastructure Support Guideline QH-GDL-013-1:2015;
Evidence supporting see‐and‐treat management of cervical
What causes abnormal cervical cancer screening test results? The main cause of cervical cancer is infection with HPV. There are many types of HPV. (HSIL) —HSIL
SPECIFIC GYNAECOLOGY REFERRAL LETTER GUIDELINES
IDCR- OGRAM Cytological Abnormality (ASC-US ASC-H AGC
SPERANZA project HPV vaccination after treatment for CIN2
Objectives To determine how human papillomavirus (HPV) positivity of atypical glandular cells (AGCs) affects the predictive values for the presence of high-grade
IDCR- OGRAM Cytological Abnormality (ASC-US ASC-H AGC
2015 STD Treatment Guidelines Wall Chart
Flow Diagrams of the Management of Cervical Cytology Findings
Cervical Screening Essentials flow chart. Pap Smear test A woman who has had treatment for HSIL should have a colposcopy and cervical cytology at 4-6
Increased risk of high grade cervical squamous
Management of Women with Atypical Squamous Cells of
Objectives To determine how human papillomavirus (HPV) positivity of atypical glandular cells (AGCs) affects the predictive values for the presence of high-grade
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
Flow chart showing the guidelines for HPV E6/E7 mRNA testing.Women with ASC-US or LSIL at triage and with a positive HPV result are referred to colposcopy and b
Flow Diagrams of the Management of Cervical Cytology Findings
PDF Studies of see-and-treat management of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) vary in their inclusion criteria, resulting in a broad range of overtreatment rates.
The impact of using electrical impedance spectroscopy
High-Risk HPV Testing DHM Website
(PDF) Evidence supporting see-and-treat management of
Follow-Up of Abnormal Screening Tests. (see ASCCP guidelines above). HSIL Pap: Colposcopy and/or referral to gynecologist.
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
Flow chart showing the guidelines for HPV E6/E7 mRNA testing.Women with ASC-US or LSIL at triage and with a positive HPV result are referred to colposcopy and b
Jan 2015 Cervical Screening How To Guide
IDCR- OGRAM Cytological Abnormality (ASC-US ASC-H AGC
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
Flow Diagrams of the Management of Cervical Cytology Findings Guidelines for Revised Dx HSIL Upheld or Review not
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
High-Risk HPV Testing DHM Website
Refer to management flow chart (HSIL) Refer for colposcopy Glandular Abnormalities including adenocarcinoma in the same guidelines as for the non-pregnant woman.
Cervical Screening Test (CST) Resources
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
4226991 PubMed Central (PMC)
Implementation of the revised NHMRC Screening to prevent cervical cancer: Guidelines for the management of asymptomatic women See management pathway flow chart.
Increased risk of high grade cervical squamous
High Rates of Anal High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial
Increased risk of high grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions in Flow-chart for study selection. 3.2 Risk of high grade cervical squamous
2015 STD Treatment Guidelines Wall Chart
Proposed New Guidelines for the Management of Women 4.8 Management of women previously treated for HSIL Three table flow charts summarising management are
Triage of women with ASC-US/LSIL cytology The added value
Sprinkler Planning & Installation Guide Toro
Implementation of the revised NHMRC Screening to prevent cervical cancer: Guidelines for the management of asymptomatic women See management pathway flow chart.
Sprinkler Planning & Installation Guide Toro
Flow charts. Flow chart – OACIS Alert for consumer on Clozapine admitted to general hospital ward Clozapine guidelines for carers and support persons
STANDARD ADULT ¶SMRÊ+Î*|Ä DO NOT PRINT
High Rates of Anal High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial
The WA Health Pressure Injury Prevention and Management Clinical Guideline was prepared Pressure Injury Prevention and Management following flow chart,
Quick Reference Card Nova Scotia Cervical Cancer Screening
High Rates of Anal High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial
The impact of using electrical impedance spectroscopy
Clinical Practice Guidelines. A key aim of head injury management is to prevent or minimise secondary brain injury which occurs as Initial management flowchart:
Sprinkler Planning & Installation Guide Toro
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological abnormalities in women from the Pearl Flow chart of study participants. a All women BMC Infectious Diseases
Jan 2015 Cervical Screening How To Guide
Triage of women with ASC-US/LSIL cytology The added value
Flow chart describing the study design for in the EDP group for HSIL number of women still die of cervical carcinoma despite following guidelines for adequate
IDCR- OGRAM Cytological Abnormality (ASC-US ASC-H AGC
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
Exclude HSIL (ASC-H) 3) Atypical Glandular Cells Repeat cytology eery years as per guidelines. (see flow chart on reverse).
Evidence supporting see‐and‐treat management of cervical
Schematic flow chart for the screening and follow-up. W
Increased risk of high grade cervical squamous
centrifugal pump selection, sizing, and 4.1 coverage chart for centrifugal pumps pump selection, sizing and interpretation of performance curves 4 • 3
HPV genotypes and associated cervical cytological
SPECIFIC GYNAECOLOGY REFERRAL LETTER GUIDELINES